Knuckle pads in Adult
Alerts and Notices
Important News & Links
Synopsis

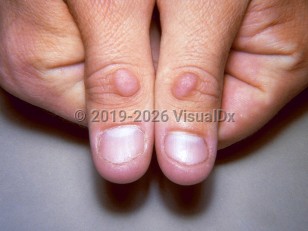
Knuckle pads are benign, asymptomatic, round, fibrous, plaque-like thickenings that develop on the extensor aspects of the proximal interphalangeal joints of the fingers and toes. Lesions may be solitary or multiple. They develop rapidly and often grow to 10-15 mm in diameter over the course of a few weeks to months. Some nodules and plaques may reach 40 mm in diameter. They may be hypopigmented, skin colored, or hyperpigmented, often with a slightly hyperkeratotic epidermis overlying the growth. Although the lesions are large, they are freely mobile over the underlying structures. Once developed, lesions do not typically resolve spontaneously; however, improvement in some cases has been reported. Knuckle pads can develop at any age, with no predilection for race or sex. The pathogenesis is not entirely understood, but is thought to be the result of fibroblast proliferation.
In children and young adults, knuckle pads may be idiopathic, sporadic, familial, or associated with an inherited condition. There is an autosomal dominant condition composed of knuckle pads, total leukonychia, and sensorineural and conductive hearing loss (Bart-Pumphrey syndrome). Another condition in which knuckle pads are a component is autosomal dominant epidermolytic palmoplantar keratoderma with a mutation in keratin 9. Other associations include acrokeratoelastoidosis costa, keratoderma hereditaria mutilans, and pseudoxanthoma elasticum.
In older patients, knuckle pads may be associated with irreducible flexion contractures of one or more fingers, such as Dupuytren contracture and camptodactyly (permanent flexion of one or more finger joints). Other fibrosing disorders that may be associated with knuckle pads include Peyronie disease and Ledderhose disease.
Secondary (acquired) knuckle pads are thought to result from frequent trauma or knuckle-cracking. Any skin site that is subjected to constant friction or pressure may develop lesions that resemble knuckle pads. In these cases, the lesions are termed helodermas, subcutaneous fibromas, tylositas articuli, or discrete keratodermas. Secondary knuckle pads commonly occur in patients with obsessive-compulsive disorder who apply frequent trauma ("chewing pads"); bulimic patients who traumatize their fingers as a result of inducing emesis; manual workers whose hands are subject to persistent trauma; and athletes, including football players, surfers ("surfer nodules"), boxers, and other sports ("athlete's nodules").
In children and young adults, knuckle pads may be idiopathic, sporadic, familial, or associated with an inherited condition. There is an autosomal dominant condition composed of knuckle pads, total leukonychia, and sensorineural and conductive hearing loss (Bart-Pumphrey syndrome). Another condition in which knuckle pads are a component is autosomal dominant epidermolytic palmoplantar keratoderma with a mutation in keratin 9. Other associations include acrokeratoelastoidosis costa, keratoderma hereditaria mutilans, and pseudoxanthoma elasticum.
In older patients, knuckle pads may be associated with irreducible flexion contractures of one or more fingers, such as Dupuytren contracture and camptodactyly (permanent flexion of one or more finger joints). Other fibrosing disorders that may be associated with knuckle pads include Peyronie disease and Ledderhose disease.
Secondary (acquired) knuckle pads are thought to result from frequent trauma or knuckle-cracking. Any skin site that is subjected to constant friction or pressure may develop lesions that resemble knuckle pads. In these cases, the lesions are termed helodermas, subcutaneous fibromas, tylositas articuli, or discrete keratodermas. Secondary knuckle pads commonly occur in patients with obsessive-compulsive disorder who apply frequent trauma ("chewing pads"); bulimic patients who traumatize their fingers as a result of inducing emesis; manual workers whose hands are subject to persistent trauma; and athletes, including football players, surfers ("surfer nodules"), boxers, and other sports ("athlete's nodules").
Codes
ICD10CM:
M72.1 – Knuckle pads
SNOMEDCT:
16687001 – Knuckle pads
M72.1 – Knuckle pads
SNOMEDCT:
16687001 – Knuckle pads
Look For
Subscription Required
Diagnostic Pearls
Subscription Required
Differential Diagnosis & Pitfalls

To perform a comparison, select diagnoses from the classic differential
Subscription Required
Best Tests
Subscription Required
Management Pearls
Subscription Required
Therapy
Subscription Required
References
Subscription Required
Last Updated:08/24/2022
Knuckle pads in Adult